|
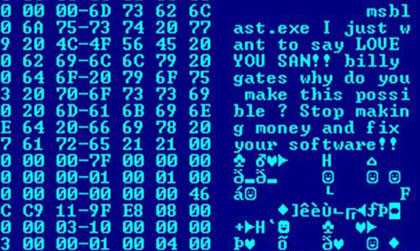
Morris Worm
The Morris worm or Internet worm of November 2, 1988, is one of the oldest computer worms distributed via the Internet, and the first to gain significant mainstream media attention. It resulted in the first felony conviction in the US under the 1986 Computer Fraud and Abuse Act. It was written by Robert Tappan Morris, a graduate student at Cornell University, and launched on 8:30 p.m. November 2, 1988, from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology network. Architecture The worm's creator, Robert Tappan Morris, is the son of cryptographer Robert Morris, who worked at the NSA. A friend of Morris said that he created the worm simply to see if it could be done, and released it from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the hope of suggesting that its creator studied there, instead of Cornell. Clifford Stoll, author of '' The Cuckoo's Egg'', wrote that "Rumors have it that orrisworked with a friend or two at Harvard's computing department (Harvard student Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Worm
A computer worm is a standalone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers. It often uses a computer network to spread itself, relying on security failures on the target computer to access it. It will use this machine as a host to scan and infect other computers. When these new worm-invaded computers are controlled, the worm will continue to scan and infect other computers using these computers as hosts, and this behaviour will continue. Computer worms use recursive methods to copy themselves without host programs and distribute themselves based on exploiting the advantages of exponential growth, thus controlling and infecting more and more computers in a short time. Worms almost always cause at least some harm to the network, even if only by consuming bandwidth, whereas viruses almost always corrupt or modify files on a targeted computer. Many worms are designed only to spread, and do not attempt to change the systems they pass thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (, ; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM ( AIX). The early versions of Unix—which are retrospectively referred to as " Research Unix"—ran on computers such as the PDP-11 and VAX; Unix was commonly used on minicomputers and mainframes from the 1970s onwards. It distinguished itself from its predecessors as the first portable operating system: almost the entire operating system is written in the C programming language (in 1973), which allows U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until he was forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the early 1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the Programmed Data Processor, PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fork Bomb
In computing, a fork bomb (also called rabbit virus) is a denial-of-service (DoS) attack wherein a process continually replicates itself to deplete available system resources, slowing down or crashing the system due to resource starvation. History Around 1978, an early variant of a fork bomb called wabbit was reported to run on a System/360 The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applicati .... It may have descended from a similar attack called RABBITS reported from 1969 on a Burroughs large systems, Burroughs 5500 at the University of Washington. Implementation Fork bombs operate both by consuming Central processing unit, CPU time in the process of Fork (system call), forking, and by saturating the operating system's process table. A basic implementation of a fork bomb is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Positives And False Negatives
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result incorrectly indicates the absence of a condition when it is actually present. These are the two kinds of errors in a binary test, in contrast to the two kinds of correct result (a and a ). They are also known in medicine as a false positive (or false negative) diagnosis, and in statistical classification as a false positive (or false negative) error. In statistical hypothesis testing, the analogous concepts are known as type I and type II errors, where a positive result corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. The terms are often used interchangeably, but there are differences in detail and interpretation due to the differences between medical testing and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Administrator
An IT administrator, system administrator, sysadmin, or admin is a person who is responsible for the upkeep, configuration, and reliable operation of computer systems, especially multi-user computers, such as Server (computing), servers. The system administrator seeks to ensure that the uptime, Computer performance, performance, System resource, resources, and Computer security, security of the computers they manage meet the needs of the User (computing), users, without exceeding a set budget when doing so. To meet these needs, a system administrator may acquire, install, or upgrade computer components and software; provide routine automation; maintain security policies; troubleshoot; train or supervise staff; or offer technical support for projects. Related fields Many organizations staff offer jobs related to system administration. In a larger company, these may all be separate positions within a computer support or Information Services (IS) department. In a smaller group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password Strength
Password strength is a measure of the effectiveness of a password against guessing or brute-force attacks. In its usual form, it estimates how many trials an attacker who does not have direct access to the password would need, on average, to guess it correctly. The strength of a password is a function of length, complexity, and unpredictability. Using strong passwords lowers the overall risk of a security breach, but strong passwords do not replace the need for other effective security controls. The effectiveness of a password of a given strength is strongly determined by the design and implementation of the authentication factors (knowledge, ownership, inherence). The first factor is the main focus of this article. The rate at which an attacker can submit guessed passwords to the system is a key factor in determining system security. Some systems impose a time-out of several seconds after a small number (e.g. three) of failed password entry attempts. In the absence of other vul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Shell
The remote shell (rsh) is a command-line computer program that can execute shell commands as another user, and on another computer across a computer network. The remote system to which ''rsh'' connects runs the ''rsh'' daemon (rshd). The daemon typically uses the well-known Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port number 513. History ''Rsh'' originated as part of the BSD Unix operating system, along with rcp, as part of the rlogin package on 4.2BSD in 1983. rsh has since been ported to other operating systems. The rsh command has the same name as another common UNIX utility, the restricted shell, which first appeared in PWB/UNIX; in System V Release 4, the restricted shell is often located at /usr/bin/rsh. As other Berkeley r-commands which involve user authentication, the rsh protocol is not secure for network use, because it sends unencrypted information over the network, among other reasons. Some implementations also authenticate by sending unencrypted pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkeley R-commands
The Berkeley r-commands are a suite of computer programs designed to enable users of one Unix system to log in or issue commands to another Unix computer via TCP/IP computer network. The r-commands were developed in 1982 by the Computer Systems Research Group at the University of California, Berkeley, based on an early implementation of TCP/IP (the protocol stack of the Internet). The CSRG incorporated the r-commands into their Unix operating system, the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The r-commands premiered in BSD v4.1. Among the programs in the suite are: (remote copy), (remote execution), (remote login), (remote shell), , , and (remote who). The r-commands were a significant innovation, and became ''de facto'' standards for Unix operating systems. With wider public adoption of the Internet, their inherent security vulnerabilities became a problem, and beginning with the development of Secure Shell protocols and applications in 1995, its adoption entirely suppla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password
A password, sometimes called a passcode, is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary String (computer science), string of character (computing), characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Login
In computer security, logging in (or logging on, signing in, or signing on) is the process by which an individual gains access to a computer system or program by identifying and authenticating themselves. Typically, user credentials consist of a username and a password. These credentials themselves are sometimes referred to as ''a'' login. Modern secure systems often require a second factor, such as email or SMS confirmation for extra security. Social login allows a user to use an existing cell phone number, or user credentials from another email or social networking service to sign in or create an account on a new website. When access is no longer needed, the user can log out, log off, sign out or sign off. Procedure Logging in is usually used to enter a specific page, website, platform or application, which trespassers cannot see. Once the user is logged in, the login token may be used to track what actions the user has taken while connected to the site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |